Expanding Therapeutic Possibilities Outside the Cell
Leveraging LYTAC Degraders for Targeted Protein Degradation
Our LYTAC platform enables targeted degradation of circulating and membrane-bound extracellular proteins. The LYTAC degradation mechanism promotes rapid, deep, and selective depletion of disease-causing extracellular proteins, many previously considered undruggable. We aim to develop LYTAC degraders into novel therapeutics for currently underserved patient populations.
Our platform is modular and flexible: LYTAC degraders can use small molecule, antibody, and other modalities to best target the specific proteins implicated in particular diseases.
What is a LYTAC?
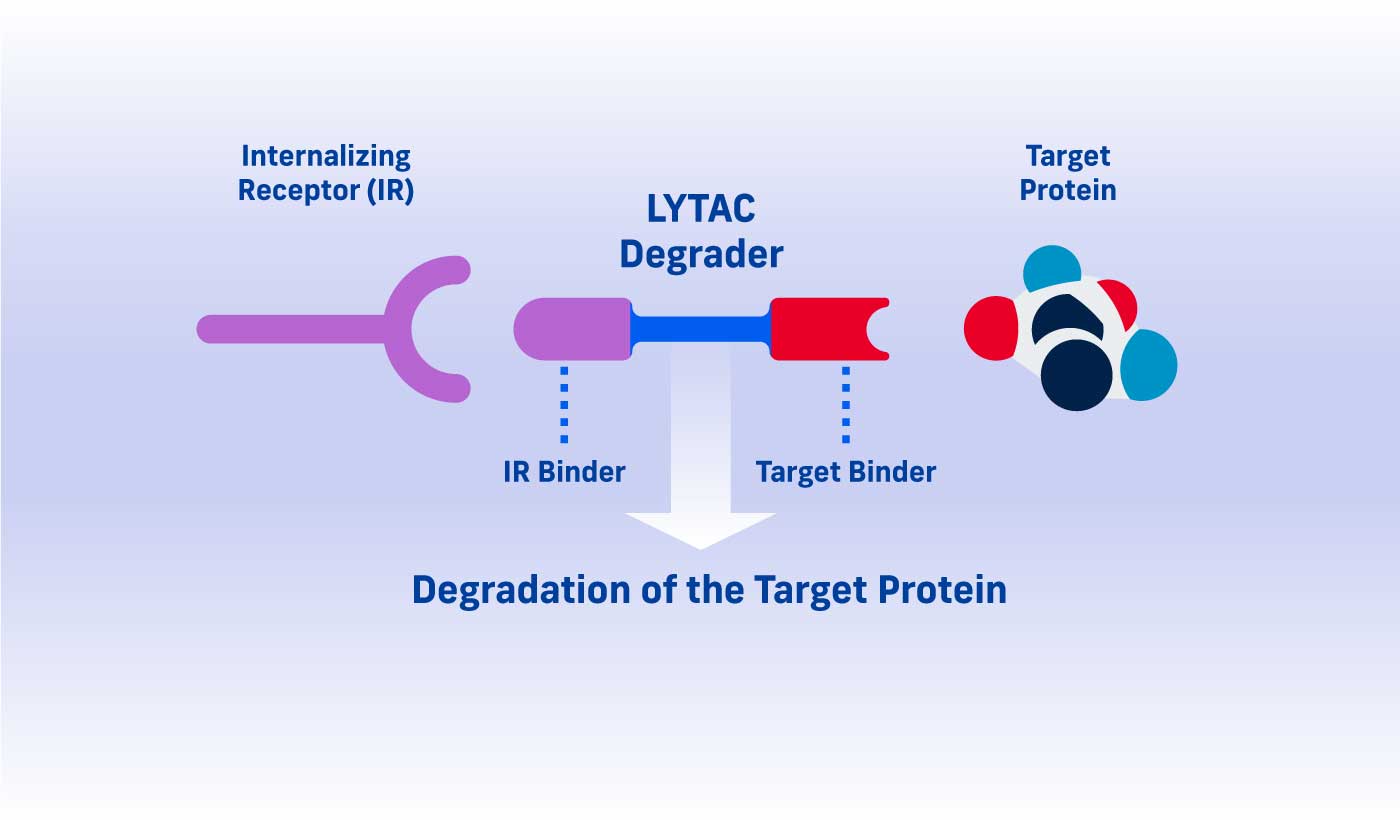
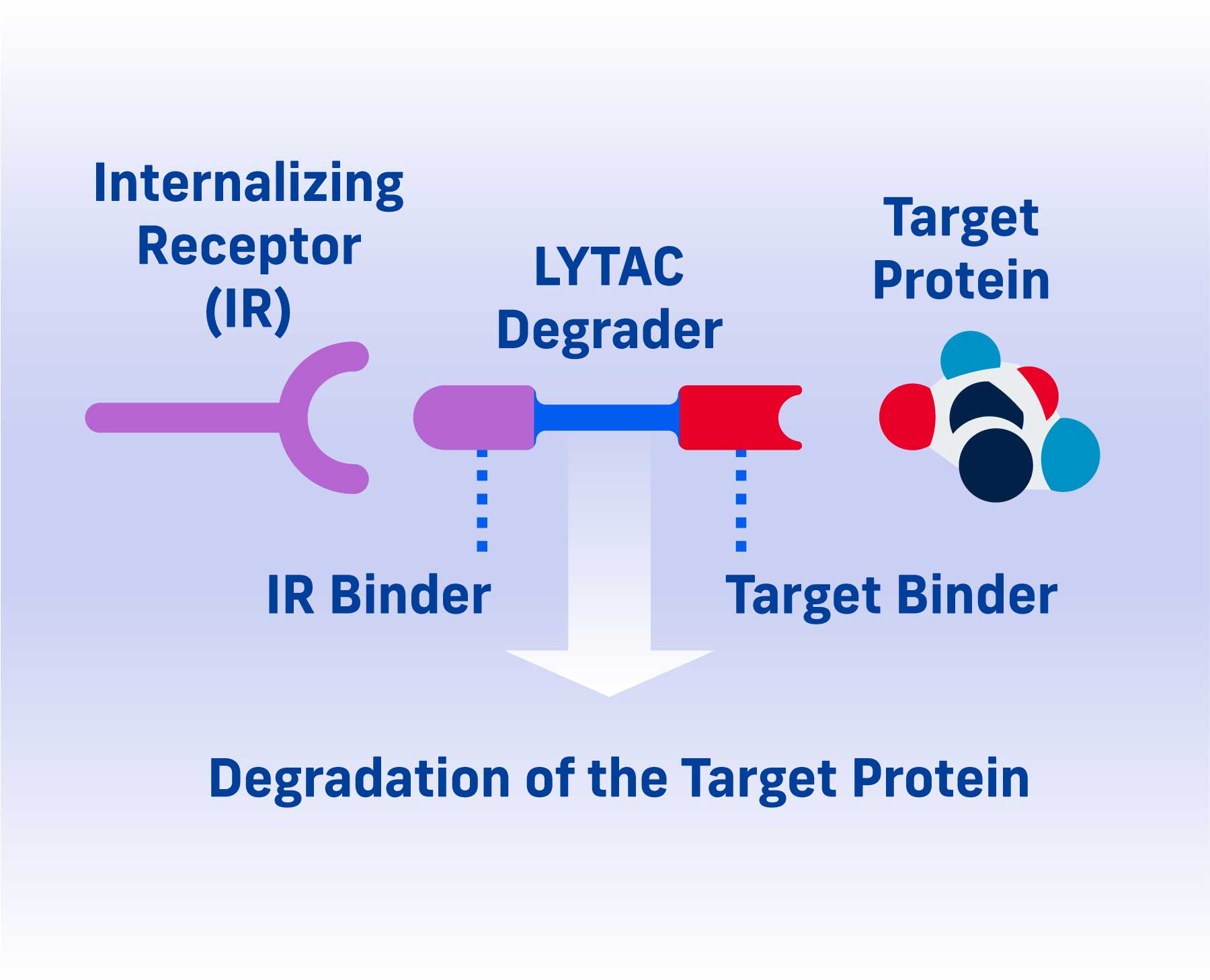
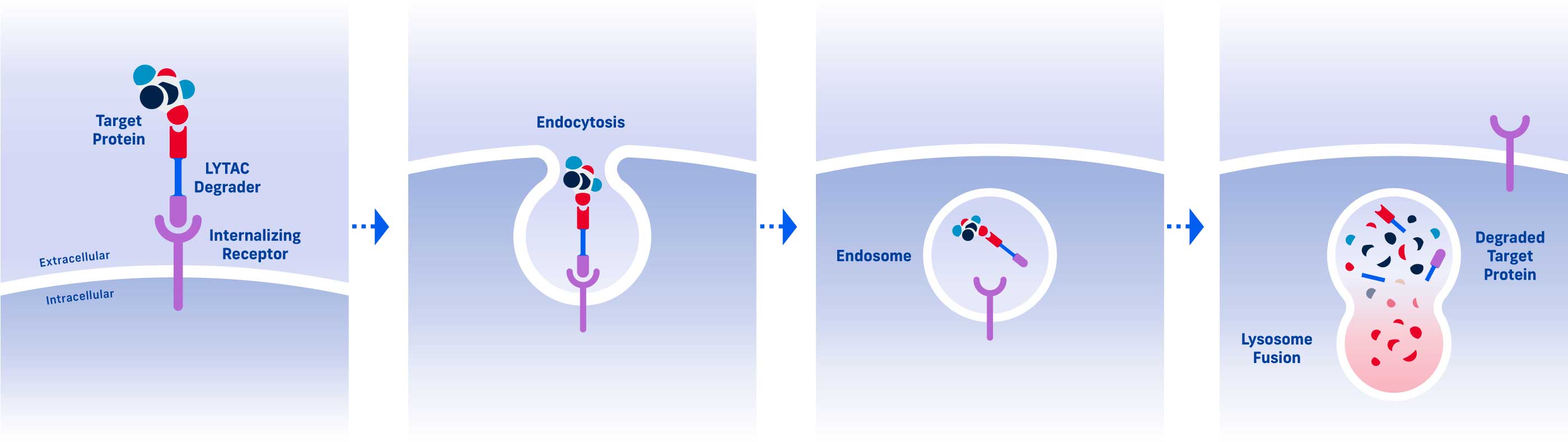
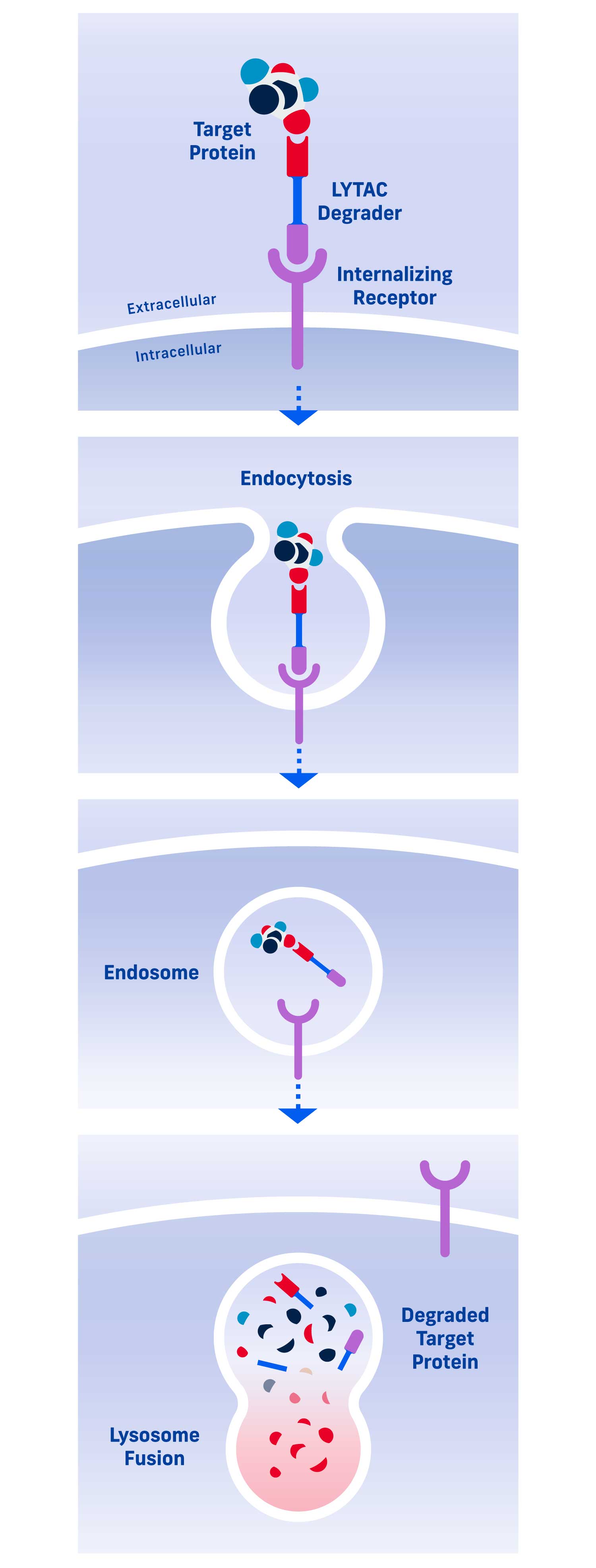
A LYTAC (Lysosomal Targeting Chimera) degrader consists of two parts: one that binds a target protein and one that binds an internalizing receptor.
By simultaneously binding a target protein and an internalizing receptor, a LYTAC degrader uses a cell’s existing trafficking systems to shuttle the target into a cell where it is degraded in the lysosome, a cellular compartment naturally responsible for protein disposal.
Dr. Carolyn Bertozzi, our founding scientist, pioneered the LYTAC concept. She and her team at Stanford University developed a new method of engineering an antibody to shuttle the target into the cell where it is degraded. Read Dr. Bertozzi’s original paper on LYTACs to understand the foundation of our technology.
The Target Binder
The target binder of a LYTAC degrader can be a small molecule, peptide, protein, or antibody, depending on what will best bind the target and limit off-target interactions. The target binder does not need to actively inhibit the target since the LYTAC degrader only requires a handle to recruit the protein to the cell for degradation.
The Internalizing Receptor
The selection of the internalizing receptor is critical to the design of a LYTAC degrader. Internalizing receptors vary in tissue expression and how they traffic to and from the cell surface. Because our LYTAC platform is amenable to a wide range of internalizing receptors, we can promote the degradation of diverse protein classes. We have designed LYTAC degraders that bind internalizing receptors for both broad-based and tissue-specific targeting.
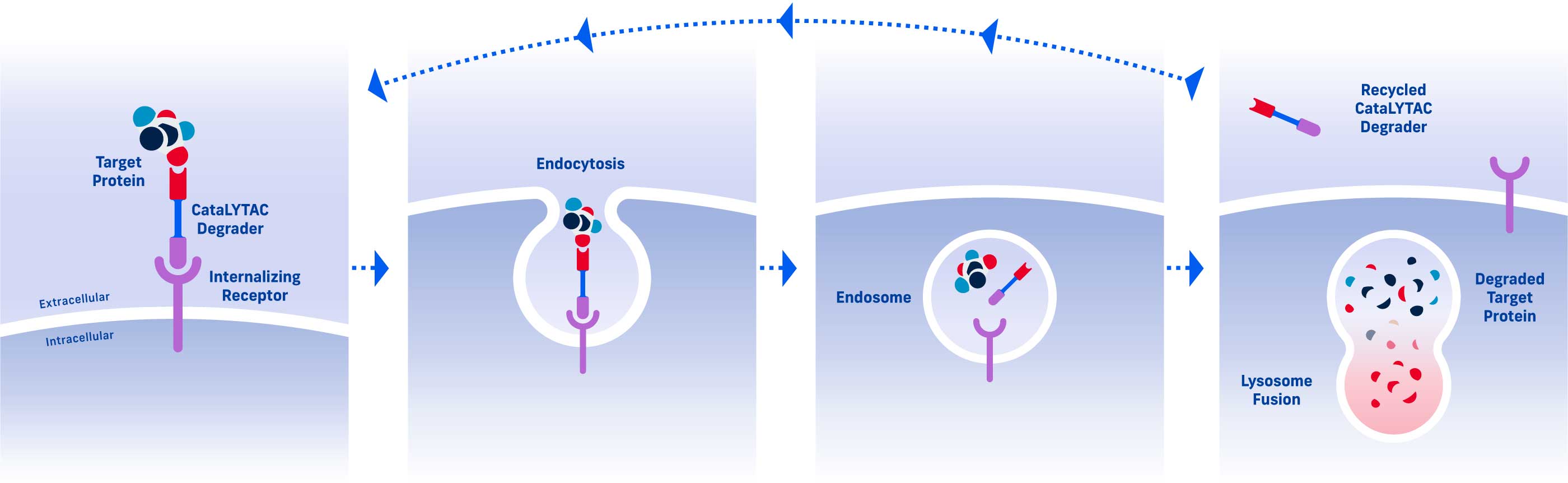
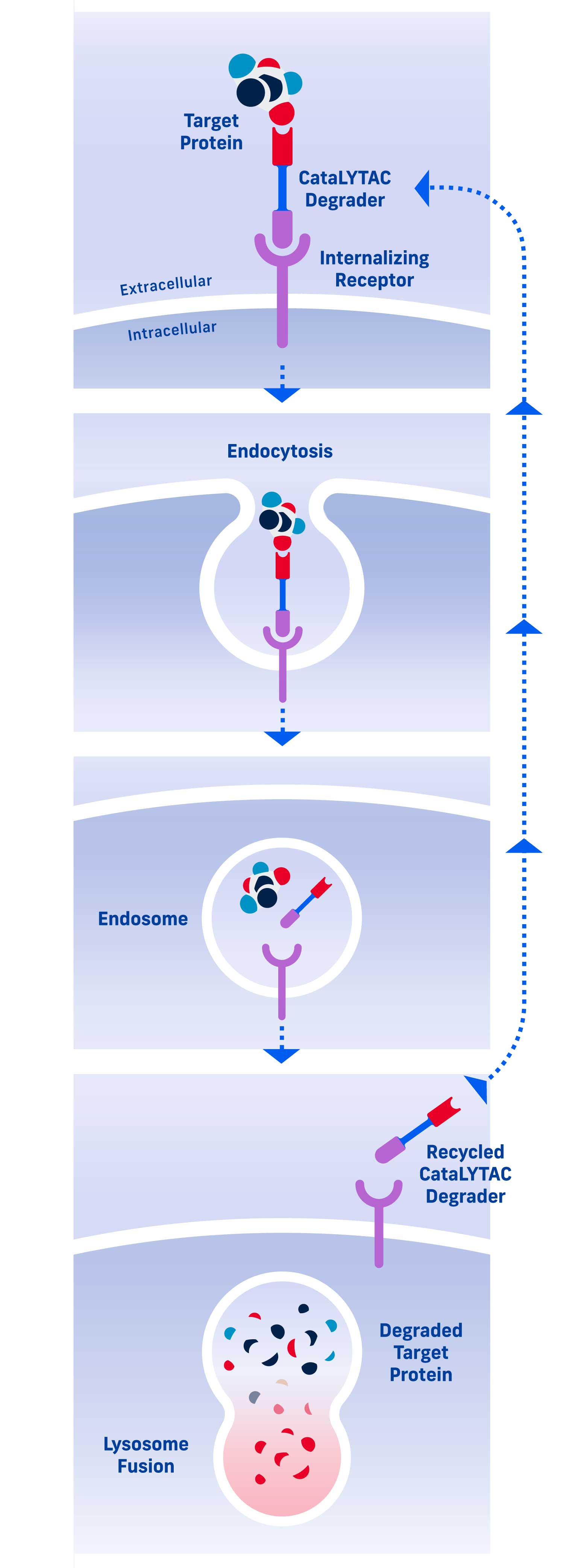
CataLYTACTM Degraders
CataLYTAC degraders repeatedly cycle into and out of a cell to promote catalytic target degradation, that is, degradation of multiple copies of a pathogenic protein per CataLYTAC degrader. CataLYTAC degraders are particularly effective for target proteins that have a high concentration or a fast resynthesis rate.
Read more about CataLYTAC Degraders here.